WRF + ParaView
Scientific robustness meets advanced VTK visualization
Python-Powered
Fully developed in Python3 for flexibility and ease of use. Yeah.
Self-Contained & Reproducible
No compilation required — ready to run out-of-the-box.
Modular Architecture
Individual modules can be extended or replaced as needed.
Future-Ready
Fully encapsulated in a reproducible Conda environment.
Seamlessly Integrated
Full access to ParaView’s powerful functionalities.
Built on Solid Foundations
Leveraging wrf-python from NCAR and optimized C-based routines.
Z-scaling – vertical exaggeration
An interactive slider allows users to dynamically adjust the vertical scaling factor of the domain. This enhances the visualization of atmospheric structures by exaggerating or compressing the vertical dimension, making boundary layers, vertical gradients, and mesoscale features easier to inspect without modifying the underlying WRF data.
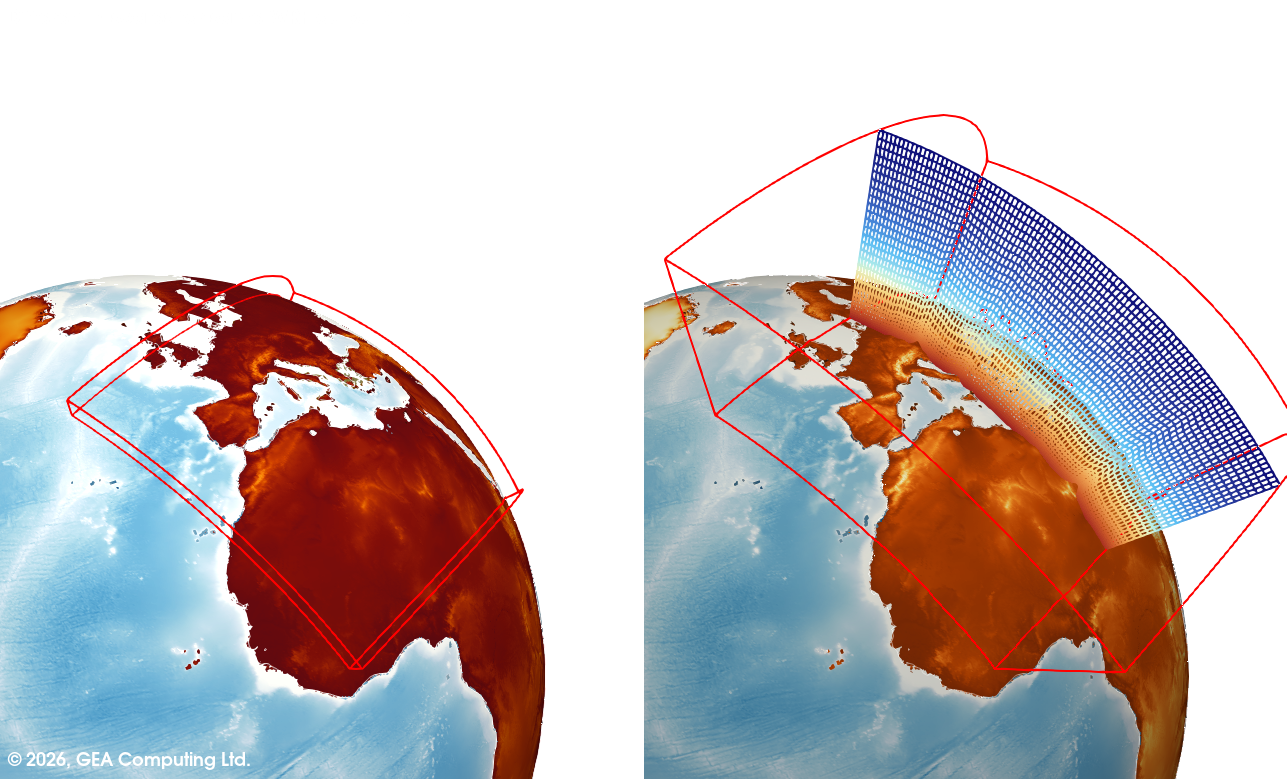
Spherical Coordinates – Conversion
Converts the model domain from Cartesian to spherical coordinates using a unit-radius sphere. This enables the visualization of WRF fields together with underlying topography mapped onto a spherical surface, allowing coherent global and large-scale atmospheric representations.
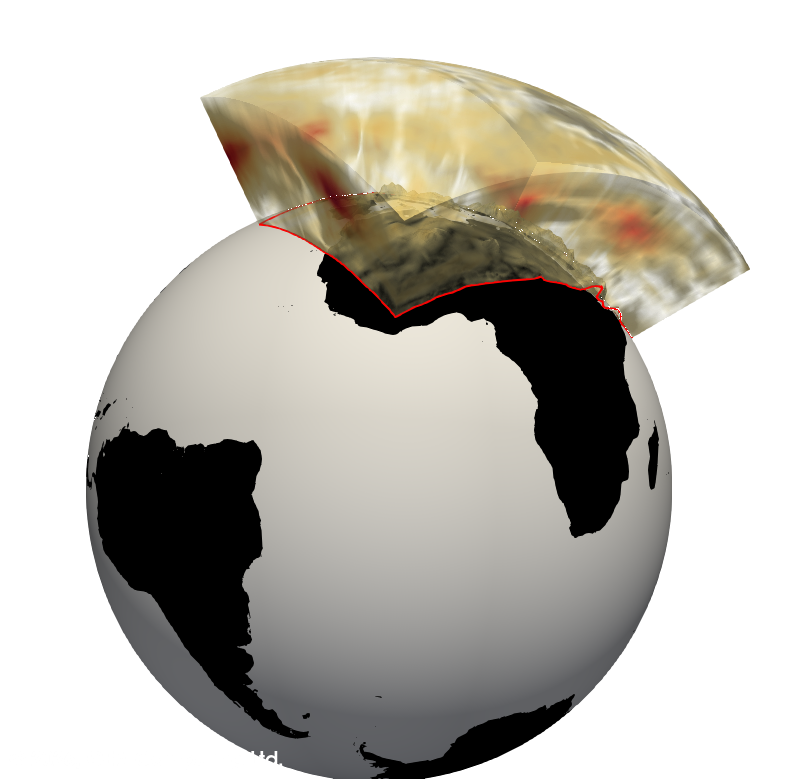
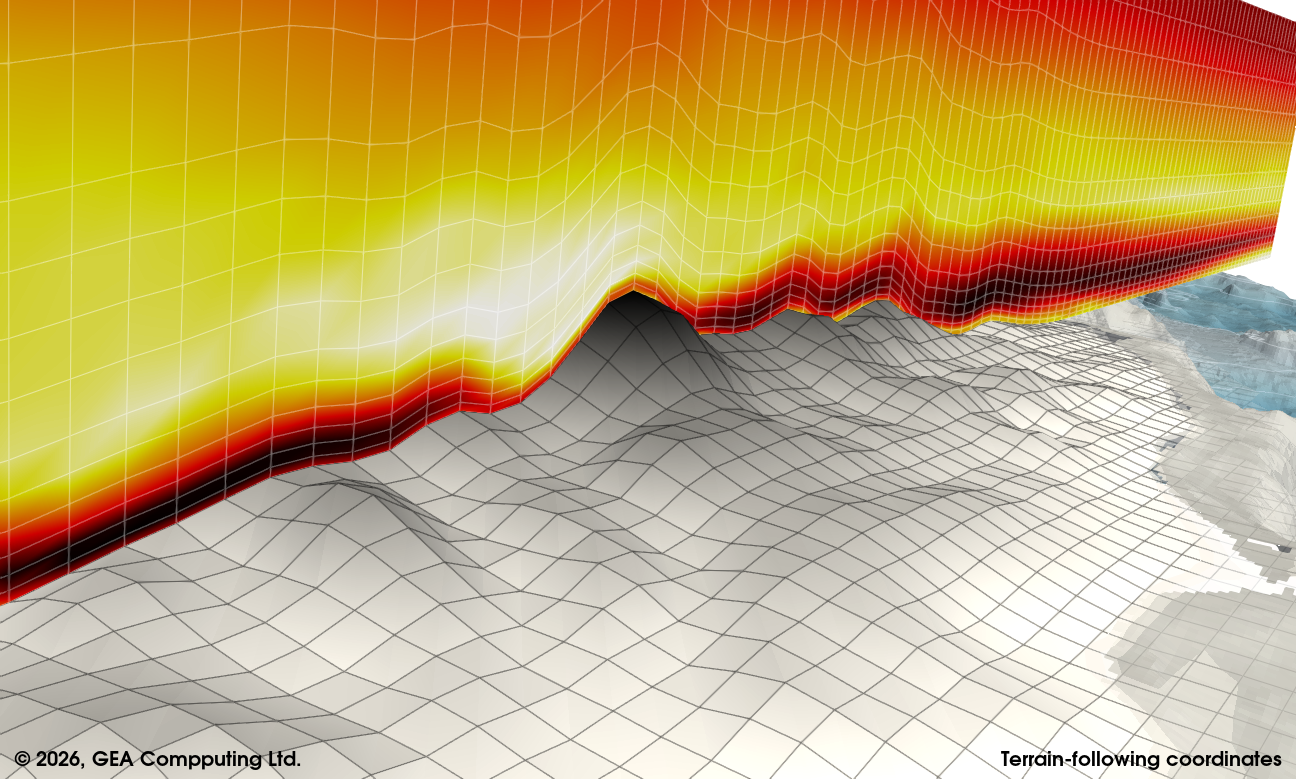
Native WRF Grid Handling
–
Accurate vertical topology
Reconstructs the native WRF grid geometry by explicitly restoring the vertical topology within ParaView. Vertical heights are computed from the differentiated geopotential fields and correctly assigned to grid points, ensuring physically consistent placement of variables in three-dimensional space.
No-Compilation Architecture
–
Conda-based extensibility
The toolkit is deployed without any source-code compilation by leveraging a dedicated Conda environment in which ParaView and WRF-Python routines are installed side by side.